
Reprodution in Plants is a chapter in Class 7 DAV science book. This Chapter revolves around the concept of the reproduction process in plants, types of reproduction methods by which plants regenerate like Vegetative Propagation, Spore formation, budding etc.
DAV Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Solutions
A. Fill in the blanks.
1. ___________ reproduce through the process of budding.
2. Pollen grains are produced by ___________.
3. The agents, that carry the pollen grains from anther to a stigma, are called ___________.
4. The fusion of a male gamete with a female gamete is called ___________.
5. Seeds of orchids get dispersed by ___________.
Answer:
(1) Yeast
(2) anther
(3) pollinators
(4) fertilisation
(5) wind
B. Write True or False for the following statements.
1. Yeast reproduces asexually through fragmentation.
2. Sweet potato and dahlia use their roots for asexual reproduction.
3. A unisexual flower has both stamen and pistil in it.
4. Water can be an agent of pollination.
5. Male and female gametes fuse to form the zygote.
6. Seeds of pea and bean plants are formed in pods.
Ans:
(1) False
(2) True
(3) False
(4) True
(5) True
(6) True
Also Check: DAV Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Solutions
C. Tick the correct option.
Ans:
1. Fragmentation
2. leaves
3. flower
4. male reproductive cell
5. ovary
DAV Class 7 Chapter 9 Solutions : Brief Questions
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
Q. 1. Name the two types of reproduction in plants.
The two types of reproduction that takes place in plants are: Asexual and Sexual Reproduction.
Q. 2. Define vegetative reproduction.
It is a method of reproduction in plants. It comes under asexual reproduction. In this method, a plant grows through the vegetative parts of the plants such as stem, roots and leaves.
Q. 3. Give two examples of plants which reproduce through spore formation.
Mosses and Ferns reproduce through spore formation.
Q. 4. Name two artificial methods of vegetative propagation from stem.
Ans. Layering: Layering is a technique of plant propagation in which the new plant remains partially attached to the main plant, forms new roots and can occur in a natural way through modified stems.
Grafting: In the process of grafting, the upper part (the scion) of a plant grows on the root system (rootstock) of other plant.
Q. 5. When is a flower said to be a bisexual flower?
Answer: A flower can be called bisexual if the plant contains both stamen and pistils part.
Q. 6. Name any three ways by which seeds are dispersed.
Answer: There are different methods for seed dispersion. Seeds can be dispersed by winds, water or through the body of animals.
Also Check: DAV Class Science Chapter 16 Solutions Water
E. Answer the following questions.
Q. 1. In what ways is vegetative propagation better than sexual reproduction?
Answer: Vegetative Propagation is better than sexual mode of reproduction in plants in many ways.
The resultant plant is an exact copy of the parent plant.
Vegetative propagation method is faster than sexual mode of reproduction in plants.
The fruits and flowers in the plant grown by vegetative propagation appeas much earlier than in sexual ones.
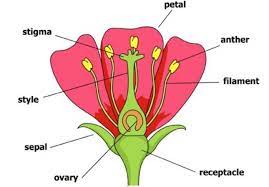
Q. 2. Draw a well labelled diagram to describe the parts of a flower.
Q. 3. How is self-pollination different from cross-pollination?
Ans. Self-pollination is a process by which pollen grains gets transferred from anther of same flower to its stigma. This can also be transferred from anther of one flower to the stigma of different flowers of same plant.
In cross-pollination, the pollen grains can be transferred from anther of one flower to the stigma of flower of a different plant.
Q. 4. How are fruits formed?
Ans: First of all fertilization process takes place in the flower resulting in formation of a zygote. Then the zygote divides multiple times and forms an embryo. A hard protective layer starts forming around the ovule. Then a seed is formed and then it converts to a grown fruit.
Q. 5. Why is dispersal of seeds necessary for growth of plants?
Ans: Dispersal of seeds is necessary because it leads to the formation of new plants from the parent plant. Dispersion is possible through wind, water and animals. It helps the new plants to grow a distant place from the parent plant. Without dispersion, plants will grow close to each other creating a situation of competition. They will then compete on the same land for nutrition, air, water and sunlight. Dispersion makes reproduction in plants smoother.
So, these were DAV Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Solutions. We have given detailed answers to Reproduction in Plants Question Answers. If you have any query, feel free to ask through the comment section below. Stay connected to CareerAdvice4u
- DAV Class 7 Science Solutions With Explanations: All Chapters - February 6, 2022
- Pollution of Water Question Answers | DAV Class 8 Science - February 4, 2022
- Fabric from Fibre Solutions | DAV Class7 Science Chapter 14 - January 25, 2022

Leave a Reply